
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Ergonomic Power Wrench Design: Optimizing Grip and Posture
- Proper Technique for Power Wrench Operation: Minimizing Strain
- Work-Rest Cycles: Scheduling Breaks to Prevent Fatigue
- Wrist Supports and Gloves: Enhancing Comfort and Protection
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Maintaining Hand and Wrist Health
- Workplace Modifications: Adjusting Workstations for Optimal Ergonomics
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Monitoring Hand and Wrist Health
- Conclusion
Protect Your Hands: Prevent Strain from Power Wrenches
Introduction
Prolonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, which can cause pain, discomfort, and reduced productivity. This introduction will provide an overview of the causes and symptoms of hand and wrist strain, as well as strategies for preventing these conditions.Ergonomic Power Wrench Design: Optimizing Grip and Posture
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Use of Power WrenchesPower wrenches are indispensable tools in various industries, but their prolonged use can lead to hand and wrist strain. To mitigate these risks, ergonomic design plays a crucial role in optimizing grip and posture.
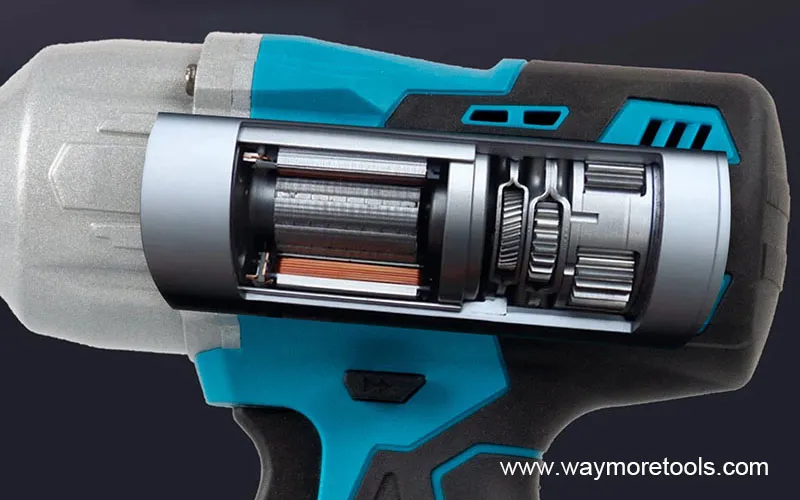
One key aspect of ergonomic power wrench design is the handle grip. A well-designed grip conforms to the natural shape of the hand, reducing pressure points and muscle fatigue. Soft, non-slip materials provide a secure and comfortable hold, minimizing the risk of slippage and strain. Additionally, adjustable grips allow users to customize the fit to their hand size, ensuring optimal comfort and control.
Another important consideration is the wrench's posture. Prolonged use of power wrenches in awkward positions can strain the wrist and forearm muscles. Ergonomic designs incorporate features that promote a neutral wrist position, reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries. For example, angled heads allow users to access hard-to-reach areas without bending their wrists excessively.
Furthermore, the weight and balance of the power wrench should be carefully considered. Heavy or unbalanced wrenches can put excessive strain on the muscles and joints. Ergonomic designs distribute weight evenly and incorporate features such as counterweights to reduce vibration and fatigue.
In addition to the physical design of the wrench, proper work practices are also essential for preventing hand and wrist strain. Regular breaks and stretching exercises help to reduce muscle tension and improve circulation. Using the wrench with the correct technique, such as applying force with the forearm rather than the wrist, can also minimize strain.
By incorporating ergonomic principles into power wrench design and promoting proper work practices, manufacturers and users can significantly reduce the risk of hand and wrist strain associated with prolonged use. This not only enhances worker safety and comfort but also improves productivity and reduces the likelihood of costly injuries.
Proper Technique for Power Wrench Operation: Minimizing Strain
**Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Power Wrench Use**Prolonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, which can cause discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. However, by following proper operating techniques, you can minimize the risk of developing these issues.
**Proper Grip and Posture**
Hold the power wrench firmly with both hands, using a neutral grip where your wrists are straight and your forearms are parallel to the ground. Avoid gripping the wrench too tightly, as this can increase strain on your hands and wrists. Maintain an upright posture with your shoulders relaxed and your elbows slightly bent.
**Use the Correct Tool for the Job**
Select a power wrench that is appropriate for the task at hand. A wrench that is too large or too small can put excessive strain on your hands and wrists. Ensure that the wrench is properly lubricated and in good working condition.
**Take Breaks and Stretch**
Regular breaks are essential to prevent muscle fatigue and strain. Take short breaks every 20-30 minutes to stretch your hands, wrists, and forearms. Simple stretches include wrist circles, finger extensions, and forearm stretches.
**Use Proper Leverage**
When using a power wrench, apply force in a smooth, controlled manner. Avoid using excessive force or jerking motions, as these can put strain on your hands and wrists. Use the wrench's leverage to your advantage by positioning it correctly and using your body weight to apply force.
**Maintain a Neutral Wrist Position**
Keep your wrists in a neutral position as much as possible. Avoid bending or twisting your wrists, as this can increase strain. If you need to change the angle of the wrench, use your whole arm to move it, rather than just your wrist.
**Use Anti-Vibration Gloves**
Anti-vibration gloves can help reduce the transmission of vibrations from the power wrench to your hands and wrists. These gloves can provide additional cushioning and support, reducing the risk of strain.
**Seek Medical Attention if Needed**
If you experience any pain or discomfort in your hands or wrists while using a power wrench, stop using it immediately and seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent more serious injuries.
By following these proper operating techniques, you can minimize the risk of developing hand and wrist strain from prolonged use of power wrenches. Remember to take breaks, stretch regularly, and use the correct tool for the job. If you experience any discomfort, seek medical attention promptly.
Work-Rest Cycles: Scheduling Breaks to Prevent Fatigue
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Use of Power Wrenches: Work-Rest Cycles for Fatigue MitigationProlonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, a common occupational hazard in industries such as construction and manufacturing. To mitigate this risk, implementing work-rest cycles is crucial. These cycles involve alternating periods of work with scheduled breaks, allowing the muscles and tendons in the hands and wrists to recover.
The duration and frequency of work-rest cycles vary depending on the intensity and duration of the work being performed. However, general guidelines recommend a 1:1 ratio, where for every hour of work, a 10-minute break is taken. During these breaks, it is essential to engage in activities that promote relaxation and reduce muscle tension, such as stretching, shaking out the hands, or massaging the wrists.
In addition to scheduled breaks, micro-breaks can also be incorporated throughout the workday. These brief pauses, lasting only a few seconds, allow for quick muscle relaxation and can be taken as needed. Micro-breaks can involve simply flexing and extending the fingers or rotating the wrists.
Proper work technique is equally important in preventing hand and wrist strain. Ensure that the power wrench is held comfortably and securely, with the wrist in a neutral position. Avoid excessive force or awkward postures that can put undue stress on the joints.
Furthermore, it is essential to maintain proper posture while using power wrenches. This includes sitting or standing with the back straight, shoulders relaxed, and elbows bent at a 90-degree angle. Good posture helps distribute weight evenly and reduces strain on the hands and wrists.
Regular hand and wrist exercises can also strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, making them less susceptible to strain. These exercises can be performed during breaks or as part of a daily routine.
In conclusion, implementing work-rest cycles, practicing proper work technique, and engaging in regular hand and wrist exercises are essential strategies for preventing hand and wrist strain from prolonged use of power wrenches. By following these guidelines, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this common occupational hazard and maintain optimal hand and wrist health.
Wrist Supports and Gloves: Enhancing Comfort and Protection
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Power Wrench UseProlonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, which can cause discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. Fortunately, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent these issues and ensure the well-being of workers.
One effective solution is the use of wrist supports. These supports provide additional stability and support to the wrist joint, reducing the strain on the muscles and tendons. They come in various designs, including elastic wraps, neoprene sleeves, and rigid braces, each offering different levels of support and protection.
Another essential preventive measure is the use of gloves. Gloves not only protect the hands from abrasions and cuts but also provide cushioning and vibration dampening. Look for gloves with ergonomic designs that minimize hand fatigue and offer a secure grip on the wrench.
Proper technique is crucial in preventing strain. Ensure that the wrench is held comfortably and securely, with the wrist in a neutral position. Avoid excessive force or awkward postures that can put undue stress on the joints.
Regular breaks are essential to prevent muscle fatigue and strain. Take short breaks throughout the day to stretch the hands, wrists, and forearms. These breaks allow the muscles to recover and reduce the risk of developing discomfort or pain.
In addition to these preventive measures, it is important to address any underlying conditions that may contribute to hand and wrist strain. Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis can make workers more susceptible to strain and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
By implementing these preventive measures, workers can significantly reduce the risk of hand and wrist strain from prolonged use of power wrenches. Wrist supports, gloves, proper technique, regular breaks, and addressing underlying conditions all play a vital role in maintaining the health and well-being of workers in various industries.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Maintaining Hand and Wrist Health
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Power Wrench UseProlonged use of power wrenches can put excessive strain on the hands and wrists, leading to discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement preventive measures, including proper stretching and strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercises help improve flexibility and range of motion in the hands and wrists. Begin by gently flexing and extending your wrists, holding each position for 10-15 seconds. Next, make circular motions with your wrists, both clockwise and counterclockwise. Finally, stretch your fingers by pulling them back towards your palm and holding for 10-15 seconds.
Strengthening exercises, on the other hand, help build muscle strength and endurance in the hands and wrists. One effective exercise is wrist curls. Hold a dumbbell or resistance band in each hand, palms facing up. Slowly curl your wrists up towards your shoulders, then lower them back down. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Another beneficial exercise is finger extensions. Place your hands on a flat surface, palms down. Spread your fingers apart and lift them off the surface, holding for 10-15 seconds. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
In addition to these exercises, it is important to take frequent breaks when using power wrenches. This allows your hands and wrists to rest and recover. During breaks, shake your hands and wrists to promote circulation and reduce stiffness.
Furthermore, proper technique is essential to minimize strain. Ensure that you are using the correct size wrench for the job and that you are gripping it firmly but not too tightly. Avoid using excessive force and take breaks as needed.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of hand and wrist strain from prolonged power wrench use. Remember to listen to your body and stop if you experience any pain or discomfort. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises, combined with proper technique and frequent breaks, will help you maintain healthy hands and wrists for years to come.
Workplace Modifications: Adjusting Workstations for Optimal Ergonomics
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Use of Power WrenchesProlonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, which can cause discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. However, there are several effective measures that can be taken to prevent these issues and ensure the well-being of workers.
Firstly, it is crucial to choose the right power wrench for the job. Wrenches with ergonomic handles and low vibration levels can significantly reduce strain on the hands and wrists. Additionally, using a torque multiplier can help reduce the amount of force required to operate the wrench, further minimizing strain.
Proper workstation setup is also essential. The wrench should be positioned at a comfortable height and angle, allowing the worker to maintain a neutral wrist position. Adjustable workstations can accommodate different user heights and preferences, ensuring optimal ergonomics.
Taking regular breaks is another important preventive measure. Short breaks throughout the day allow the muscles and tendons in the hands and wrists to rest and recover. During these breaks, it is beneficial to perform hand and wrist stretches to promote circulation and reduce tension.
Wearing proper gloves can also provide support and protection for the hands and wrists. Gloves with padded palms and reinforced fingertips can absorb vibrations and reduce friction, minimizing strain and discomfort.
In addition to these measures, it is essential to train workers on proper power wrench usage techniques. This includes demonstrating the correct grip, posture, and work practices to minimize strain. Regular training sessions can reinforce these techniques and ensure that workers are using the wrenches safely and effectively.
By implementing these preventive measures, employers can significantly reduce the risk of hand and wrist strain among workers who use power wrenches. These measures not only enhance worker comfort and well-being but also contribute to increased productivity and reduced absenteeism due to work-related injuries.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Monitoring Hand and Wrist Health
Preventing Hand and Wrist Strain from Prolonged Power Wrench UseProlonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, which can cause discomfort, pain, and even long-term damage. To prevent these issues, it is crucial to take proactive measures to protect your hands and wrists.
Regular medical check-ups are an essential part of maintaining hand and wrist health. During these check-ups, your doctor can assess your hands and wrists for any signs of strain or injury. They can also provide guidance on proper tool use and recommend exercises to strengthen your hands and wrists.
In addition to regular check-ups, there are several other steps you can take to prevent hand and wrist strain from power wrench use. First, it is important to use the correct technique when operating a power wrench. This includes holding the wrench firmly with both hands and keeping your wrists straight.
Second, it is important to take breaks throughout the day to give your hands and wrists a chance to rest. During these breaks, you can stretch your hands and wrists and apply ice packs to reduce inflammation.
Third, it is important to use power wrenches that are the correct size for your hands. Using a wrench that is too large or too small can put unnecessary strain on your hands and wrists.
Finally, it is important to listen to your body and stop using the power wrench if you experience any pain or discomfort. Ignoring pain can lead to more serious injuries.
By following these tips, you can help prevent hand and wrist strain from prolonged use of power wrenches. Regular medical check-ups, proper tool use, and taking breaks throughout the day are all essential for maintaining hand and wrist health.
Conclusion
**Conclusion:**Prolonged use of power wrenches can lead to hand and wrist strain, but there are several effective measures that can be taken to prevent these injuries. These include using proper technique, taking frequent breaks, using ergonomic tools, and strengthening the muscles in the hands and wrists. By following these recommendations, workers can reduce their risk of developing hand and wrist strain and maintain optimal health and productivity.
 Waymore Tools
Waymore Tools

















































































































































































Leave a Comment